In this article, we will see how to create a User-Defined function in Kotlin. Along with that, we will learn how to add two numbers using a function in Kotlin.
fun AddTwoNumbers(x: Int, y: Int) : Int {
val c = x + y
return c;
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val sum: Int
sum = AddTwoNumbers(6, 3)
println("Sum of two number is:$sum")
}
val c = x + y
return c;
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val sum: Int
sum = AddTwoNumbers(6, 3)
println("Sum of two number is:$sum")
}
Output:
Sum of two number is: 9
Sum of two number is: 9
How to create a User-Defined function in Kotlin?
"fun" keyword is used to defined function in Kotlin. Then comes an identifier name, which is a function name. In this example, function(identifier) name is AddTwoNumbers.
In the above example, this function does have two arguments of type Int. Here the definition of a function is AddTwoNumbers(x: Int, y: Int).
The code is written inside curly braces {}, which is known as a body of a function.
How to get return Value from a function in Kotlin?
In Kotlin, Void is the default return type of the function, if it is not intentionally defined. In above example fun AddTwoNumbers(x: Int, y: Int) : Int, Integer is the return type of function.
How to call a function in Kotlin?
To call a function in Kotlin, just write a function name and pass the parameters of argument type mentioned.
In the above example, function AddTwoNumbers(6, 3) is called inside the main method. The value returned from a function is stored in a variable called sum.



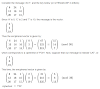





0 Comments